Overview
Ginger, a versatile and widely-used spice, boasts a rich history and numerous applications across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into everything about ginger, from its diverse types and nutritional values to its advanced production techniques, market dynamics, and innovative uses, providing a thorough understanding of this remarkable plant.
Ginger Product Overview
Types and Varieties of Ginger
Ginger comes in various types and varieties, each with unique characteristics, flavors, and uses. The most common varieties include:
- Common Ginger (Zingiber officinale): The most widely available variety, recognized for its knobby rhizomes with tan skin and pale yellow flesh. Its flavor profile ranges from mildly sweet and citrusy to intensely spicy and warm, depending on the origin and processing.
- Young Ginger: Harvested earlier in the growing season, young ginger boasts a more delicate flavor and tender texture. Its pale, almost translucent skin and juicy flesh make it ideal for pickling and candying.
- Blue Ring Ginger: This variety is easily identifiable by the distinctive blue ring that appears just beneath its skin. Its flavor is similar to common ginger, but with a slightly milder, sweeter edge.
- Yellow Ginger: Known for its bright yellow flesh, yellow ginger offers a more pungent and spicy kick than common ginger. It’s often used in savory dishes and traditional medicine.
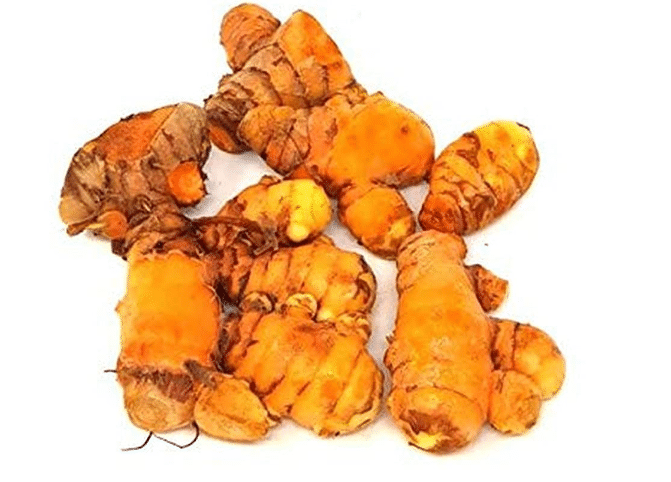



To learn more about the different types of ginger, we recommend this guide:Ginger Mania: 7 Unique Flavors You’ll Absolutely Love
Nutritional Value
Beyond its culinary versatility, ginger boasts an impressive nutritional profile, packed with vitamins, minerals, and potent bioactive compounds.
| Nutrient | Amount per 100g | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 80 | Relatively low in calories, making it a healthy addition to a balanced diet. |
| Carbohydrates | 17.8 g | Primarily in the form of starches, providing energy. |
| Protein | 1.8 g | Contributes to a small amount of protein. |
| Fiber | 2 g | Supports digestive health and regularity. |
| Vitamin C | 5 mg | An antioxidant that supports immune function and skin health. |
| Magnesium | 43 mg | Essential for muscle function, nerve function, and blood sugar control. |
| Potassium | 415 mg | An electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance and blood pressure. |
| Manganese | 0.2 mg | A trace mineral involved in bone health, metabolism, and antioxidant defense. |
| Gingerol | Varies | The primary bioactive compound in ginger, responsible for its pungent flavor and numerous health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. |
| Shogaol | Varies | A bioactive compound formed when ginger is heated or dried, also exhibiting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. |
| Zingerone | Varies | Another bioactive compound found in ginger, known for its antioxidant and potential anti-cancer properties. |
Gingerol, the primary bioactive compound in ginger, is responsible for its distinct flavor and numerous health benefits. Studies suggest that gingerol possesses potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, potentially aiding in:
- Nausea and Vomiting Relief: Ginger has long been used as a natural remedy for nausea, particularly during pregnancy and chemotherapy.
- Digestive Support: Ginger can help soothe digestive discomfort, reduce bloating, and promote healthy digestion.
- Pain Management: The anti-inflammatory properties of ginger may help alleviate muscle soreness, menstrual cramps, and osteoarthritis pain.
- Immune System Boost: Ginger’s antioxidant properties may help strengthen the immune system and protect against oxidative stress.
Want to learn more about Ginger’s Nutritional Value? Please go to Ginger’s 10 Powerful Nutrients.
Main Uses
Health Benefits of Ginger
Ginger is renowned for its numerous health benefits, many of which are attributed to its bioactive compounds like gingerol and shogaol. Here are some of the key health benefits:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Ginger contains potent anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce inflammation and can alleviate symptoms of arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
- Antioxidant Effects: The antioxidants in ginger help combat oxidative stress and reduce cell damage, which can protect against chronic diseases.
- Digestive Aid: Ginger is widely used to treat various forms of nausea, including morning sickness, motion sickness, and chemotherapy-induced nausea. It also aids digestion and can help relieve indigestion and bloating.
- Pain Relief: Ginger has been shown to be effective in reducing muscle soreness and pain, including menstrual pain. Its anti-inflammatory properties also contribute to pain reduction.
- Cardiovascular Health: Ginger may help lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and improve overall heart health by preventing the formation of blood clots and reducing arterial stiffness.
- Immune Support: The bioactive compounds in ginger can boost the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively.
Detailed introduction:https://sinogarlics.com/gingers-gold-10-health-benefits-you-need-to-know/
Culinary Uses of Ginger
Ginger is a staple in kitchens around the world, prized for its unique flavor and versatility. Here are some common culinary uses:
- Fresh Ginger: Fresh ginger is often used in stir-fries, soups, and marinades. It can also be grated or sliced and added to teas and smoothies for a spicy kick.
- Dried or Powdered Ginger: Dried ginger is a key ingredient in baking, used in recipes like gingerbread, cookies, and cakes. It is also used in spice blends and curries.
- Pickled Ginger: Often served with sushi, pickled ginger (also known as gari) is a common palate cleanser. It can also be used in salads and sandwiches for added zest.
- Ginger Juice: Extracted from fresh ginger, ginger juice is used in beverages, dressings, and sauces. It adds a refreshing and spicy note to drinks and dishes.
- Candied Ginger: Candied ginger is ginger that has been cooked in sugar syrup and dried. It’s a popular sweet treat and can be used in baking or eaten on its own.
- Ginger Tea: Made by steeping fresh ginger slices in hot water, ginger tea is a soothing beverage often consumed to relieve digestive issues and colds.
Detailed introduction:https://sinogarlics.com/ginger-versatility-the-incredible-industrial-uses/
Applications of Ginger in Alternative Medicine
Ginger has a long history of use in alternative medicine, particularly in Ayurvedic and Traditional Chinese Medicine. Here are some of its applications:
- Nausea and Vomiting: Ginger is highly effective in treating nausea and vomiting, including morning sickness during pregnancy and nausea caused by chemotherapy.
- Cold and Flu Relief: Ginger is commonly used to alleviate symptoms of colds and flu, such as sore throat, congestion, and coughing. Its warming properties help to soothe and heal.
- Digestive Health: Ginger is used to support overall digestive health, treating conditions like indigestion, gas, and bloating. It stimulates digestion and helps improve gut motility.
- Anti-inflammatory Treatments: Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, ginger is used to treat inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Pain Management: Ginger is used as a natural remedy for pain relief, including menstrual pain, joint pain, and muscle soreness. Its analgesic properties make it a popular choice for pain management.
- Metabolic Support: Ginger is believed to boost metabolism and support weight management. It is often included in detox diets and weight loss programs.
- Immune Boosting: Ginger’s immune-boosting properties make it a common ingredient in immune support supplements and herbal remedies to prevent and treat infections.
A Global Commodity: Ginger Trade and Market Trends
Production Powerhouses:
While ginger is cultivated in various tropical and subtropical regions, a few countries dominate global production:
- India: Holding the title of the world’s largest ginger producer, India accounts for approximately 30-35% of global production, known for its high-quality ginger varieties. In 2021, India produced an estimated 2.8 million metric tons of ginger.
- China: A major player in the ginger market, China produces around 20-25% of the world’s ginger, with a focus on both fresh and processed forms. In 2021, China’s ginger production was estimated at 1.8 million metric tons.
- Nigeria: Emerging as a key ginger producer, Nigeria has witnessed substantial growth in its ginger exports in recent years, currently contributing to about 10-15% of global production.
- Other Producers: Countries like Indonesia, Nepal, Thailand, and Cameroon also contribute to the global ginger supply chain, each producing a few hundred thousand metric tons annually.
Get more information on the ginger Production Powerhouses at Top 5 Ginger Production Powerhouses.
Trade Flows and Market Demand:
- Major Importers: The demand for ginger is robust in countries with established culinary traditions and growing health-conscious populations. The United States is the world’s largest importer of ginger, followed by European Union countries, particularly the Netherlands, Germany, and the United Kingdom. Other key importers include Japan, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Emerging Markets: As awareness of ginger’s health benefits grows, new markets are emerging, particularly in regions with developing economies and increasing interest in natural and organic products. This includes countries in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and Africa.
- Market Size and Growth: The global ginger market size was valued at USD 4.1 billion in 2021 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2022 to 2030, according to Grand View Research, Inc.
- Market Drivers: Several factors fuel the global ginger trade:
- Culinary Demand: Ginger remains a staple ingredient in numerous cuisines, driving consistent demand for both fresh and processed forms.
- Health and Wellness Trends: The increasing consumer interest in natural remedies and functional foods has boosted the demand for ginger, particularly in its raw and minimally processed forms. The global functional food market, of which ginger is a part, is expected to reach USD 341.4 billion by 2027, according to Statista.
- Growing Application in Various Industries: The use of ginger extracts in food processing, beverages, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals further contributes to market growth.
Get more information on the ginger market at
- The Future of Chinese Ginger: Exciting Trends and Opportunities Ahead
- 3 Pillars of Success in the Global Ginger Market:Dynamics, Trends, Essentials
- Ginger E-commerce: the 7 Core Advantages
Why choose CAIE for your ginger supplier?
- Vertical Integration: CAIE has an integrated business model covering the entire supply chain from farming to warehousing, logistics, and export. This vertical integration allows for better quality control, traceability, and efficiency throughout the process.
- Dedicated Ginger Farms: CAIE owns over 10,000 acres of farms in Weifang City, which is considered the home of ginger production in China. This direct access to prime ginger growing regions ensures a reliable and high-quality supply of fresh ginger.
- Adherence to International Standards: CAIE follows stringent international standards, including those of the European Union, Japan, and the United States, for soil analysis, seed selection, planting, and harvesting practices. This commitment to rigorous standards guarantees top-quality ginger products.
- Modern Infrastructure: CAIE has over 100,000 square meters of modern, climate-controlled warehouses in the ginger production regions, ensuring optimal storage conditions and preservation of ginger quality from harvest to export.
- Bonded Logistics Expertise: CAIE has a specialized bonded logistics team in the Weifang Free Trade Zone, facilitating smooth and efficient export processes while maintaining product quality throughout the supply chain.
- Extensive Export Experience: Through the acquisition of Weifang Xinyide Agriculture Science and Technology Co., Ltd., CAIE has gained a professional team with over 20 years of experience in exporting agricultural products, including ginger.
- Government Support: CAIE benefits from policy support from the local governments of Shandong Province and Weifang City, which enhances its competitive advantage in areas such as planting, warehousing, and bonded logistics.
- Global Reach: CAIE has established relationships with over 30 large-scale buyers from 19 countries across Southeast Asia, Japan, Europe, and North America, demonstrating its ability to serve a diverse global customer base effectively.
- Variety and Volume: With its extensive resources and infrastructure, CAIE can provide larger quantities of various ginger varieties to meet the diverse needs of buyers worldwide.
By choosing CAIE as their ginger supplier, buyers can benefit from a reliable, high-quality supply chain backed by extensive expertise, modern infrastructure, and government support, ensuring a consistent and efficient ginger sourcing experience.
- Why choose CAIE
- Why Choose China(Ginger Suppliers)
- Direct to product page:https://sinogarlics.com/product-category/ginger/.
FAQ
1. What are the key health benefits of consuming ginger regularly?
Answer: Ginger offers numerous health benefits due to its bioactive compounds like gingerol and shogaol. Regular consumption can help reduce inflammation, provide antioxidant effects, aid digestion, relieve pain, support cardiovascular health, and boost the immune system.
2. How can I incorporate ginger into my daily diet?
Answer: Ginger can be incorporated into your diet in various ways:
- Add fresh ginger to stir-fries, soups, and marinades.
- Use dried or powdered ginger in baking, spice blends, and curries.
- Drink ginger tea by steeping fresh ginger slices in hot water.
- Use ginger juice in beverages, dressings, and sauces.
- Enjoy candied ginger as a sweet treat or in baking.
3. Can ginger help with nausea and digestive issues?
Answer: Yes, ginger is highly effective in treating nausea, including morning sickness, motion sickness, and chemotherapy-induced nausea. It also aids digestion and can help relieve indigestion, bloating, and gas by stimulating digestive enzymes and improving gut motility.
4. Are there any side effects or precautions to consider when consuming ginger?
Answer: While ginger is generally safe for most people, excessive consumption can lead to side effects such as heartburn, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort. People on blood-thinning medications should consult their healthcare provider before using ginger supplements, as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
5. How is ginger used in alternative medicine?
Answer: In alternative medicine, ginger is used to treat a variety of conditions:
- Relieves nausea and vomiting.
- Alleviates cold and flu symptoms.
- Supports digestive health and treats indigestion.
- Reduces inflammation in conditions like arthritis.
- Provides natural pain relief for menstrual cramps and muscle soreness.
- Boosts metabolism and supports weight management.
- Enhances immune function to prevent and treat infections.
