GingembreLe gingembre, avec son piquant et sa nature polyvalente, s'est assuré une place de choix sur le marché mondial. Cette analyse se penche sur les subtilités du commerce du gingembre, en examinant la dynamique du marché, les préférences des consommateurs et les exigences essentielles en matière d'exportation pour les négociants en gingembre en herbe.
Commerce mondial du gingembre : Un aperçu du paysage actuel
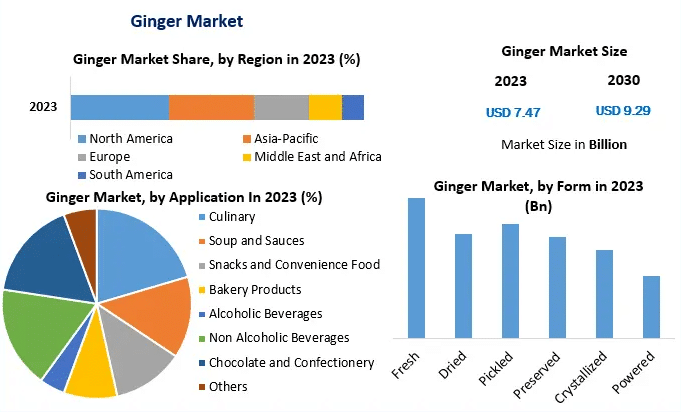
Le marché mondial du gingembre connaît une croissance robuste, alimentée par l'augmentation des applications culinaires, la prise de conscience des problèmes de santé et la préférence croissante pour les aliments naturels et biologiques. Voici un aperçu de la dynamique commerciale actuelle :
- Les centrales de production : L'Asie domine la production mondiale de gingembre, avec l'Inde, la Chine, le Nigeria et l'Indonésie en tête.
- Principales destinations d'exportation : Les États-Unis, les pays de l'Union européenne, le Japon et les pays du Moyen-Orient sont de grands importateurs de gingembre, ce qui alimente la demande pour cette épice polyvalente.
- Valeur de marché : Le marché mondial du gingembre est estimé à plusieurs milliards de dollars et les projections indiquent une croissance continue dans les années à venir.

Décoder les préférences des consommateurs : Quels sont les moteurs de la demande de gingembre ?
Comprendre les préférences des consommateurs est essentiel pour réussir dans le commerce du gingembre. Voici une analyse des facteurs clés qui déterminent la demande sur les principaux marchés :
1. L'Ouest : La saveur et le bien-être à l'honneur
- Exploration culinaire : Les consommateurs occidentaux sont de plus en plus audacieux, incorporant le gingembre dans un plus grand nombre de plats, des sautés d'inspiration asiatique aux smoothies et aux desserts.
- Halo de la santé : La réputation du gingembre en tant que remède naturel contre les nausées, les problèmes digestifs et l'inflammation a renforcé sa popularité en tant qu'aliment de santé et ingrédient dans les compléments alimentaires et les boissons.
- Choix biologiques et durables : Le consumérisme éthique est en plein essor, avec un segment croissant de consommateurs occidentaux qui recherchent du gingembre issu de l'agriculture biologique et de l'agriculture durable.
2. Asie : Utilisations traditionnelles et évolution des goûts
- Un produit de base pour la cuisine : Le gingembre est profondément ancré dans les cuisines asiatiques traditionnelles. Il est largement utilisé dans les currys, les sautés, les soupes et les boissons.
- Héritage médicinal : Les pratiques ayurvédiques et la médecine traditionnelle chinoise continuent de stimuler la demande de gingembre en tant que remède naturel contre diverses affections.
- Applications modernes : Les marchés asiatiques connaissent également une augmentation des produits innovants à base de gingembre, tels que les bonbons au gingembre, les snacks et les boissons, afin de répondre à l'évolution des goûts.
Exporter du gingembre : Emballage, transport et conformité
Pour réussir sur le marché de l'exportation du gingembre, il faut respecter des normes de qualité strictes et se conformer aux réglementations internationales.
1. Conditionnement pour la conservation :
- Contrôle de l'humidité : Le gingembre est sensible aux moisissures et à la détérioration, d'où l'importance d'un emballage adéquat. Les matériaux d'emballage hermétiques qui empêchent l'absorption de l'humidité sont essentiels pour préserver la fraîcheur.
- Régulation de la température : Le gingembre se conserve et se transporte de préférence à des températures fraîches afin d'en préserver la qualité. Des conteneurs réfrigérés ou un stockage sous atmosphère contrôlée peuvent être nécessaires, en fonction de la distance et de la durée du transport.
- Exigences en matière d'étiquetage : Un étiquetage clair et précis est essentiel, comprenant des informations sur le produit, son origine, son poids et toutes les certifications nécessaires (par exemple, biologique, commerce équitable).
2. Le transport : Garantir une livraison en temps voulu :
- Mode de transport : Le choix du mode de transport (fret maritime, fret aérien) dépend de facteurs tels que la destination, le budget et le délai de livraison souhaité.
- Contrôle de la température : Le maintien d'une température optimale tout au long du voyage est essentiel pour éviter toute détérioration. Des conteneurs réfrigérés ou des camions à température contrôlée peuvent être nécessaires.
- Manipulation et stockage : Une manipulation adéquate lors du chargement, du déchargement et du stockage dans les ports ou les centres de distribution est essentielle pour minimiser les dommages et préserver la qualité du gingembre.
3. Conformité : Respecter les normes internationales :
- Exigences phytosanitaires : Les pays exportateurs doivent se conformer aux réglementations phytosanitaires des pays importateurs afin d'empêcher la propagation des maladies et des parasites des plantes. Cela peut impliquer des inspections, des traitements et des certifications.
- Normes de sécurité alimentaire : Le respect des normes internationales de sécurité alimentaire, telles que l'HACCP (analyse des risques et maîtrise des points critiques), est essentiel pour garantir la sécurité et la qualité du gingembre destiné à la consommation.
- Droits et tarifs à l'importation : Les exportateurs doivent être conscients des droits de douane et des tarifs imposés par les pays importateurs, car ils peuvent avoir une incidence sur les prix et la compétitivité.
Tirer parti du boom du gingembre : conseils pour réussir
- Étude de marché : Mener des recherches approfondies pour identifier les marchés cibles, comprendre les préférences des consommateurs et analyser les activités des concurrents.
- Assurance qualité : Mettre en œuvre des mesures rigoureuses de contrôle de la qualité tout au long de la chaîne d'approvisionnement, de la culture à l'emballage, afin de garantir un gingembre de qualité supérieure.
- Pratiques durables : Adopter des méthodes d'agriculture et de transformation durables pour attirer les consommateurs soucieux de l'environnement et garantir la viabilité à long terme.
- Ajout de valeur : Étudier les possibilités de développer des produits à base de gingembre à valeur ajoutée, tels que la poudre de gingembre, l'huile de gingembre ou les en-cas infusés au gingembre, afin de diversifier l'offre et d'améliorer la rentabilité.
- Établir des relations : Établir des relations solides avec les acheteurs, les importateurs et les distributeurs sur les marchés cibles afin de garantir le bon déroulement des opérations commerciales.
Préférences des consommateurs et demande sur les marchés clés
États-Unis
Préférences :
- Gingembre frais : Le gingembre frais fait l'objet d'une forte préférence en raison de sa polyvalence en cuisine et de ses bienfaits perçus pour la santé.
- Produits de santé à base de gingembre : Les consommateurs recherchent de plus en plus le gingembre dans divers produits de santé, tels que les thés, les compléments et les shots de bien-être, en raison de ses bienfaits anti-inflammatoires et digestifs.
- Utilisations culinaires : Le gingembre est un ingrédient populaire tant dans les recettes traditionnelles que dans la cuisine fusion moderne. Il est utilisé dans tous les domaines, des sautés aux marinades, en passant par les pâtisseries et les boissons.
Tendances :
- Gingembre biologique et issu de l'agriculture durable : La demande de gingembre biologique est en hausse, car les consommateurs sont de plus en plus soucieux de leur santé et de l'environnement.
- Produits de commodité : Le marché des produits au gingembre prêts à l'emploi, tels que le gingembre haché, les pâtes de gingembre et les poudres de gingembre, est en pleine expansion et répond aux besoins des personnes pressées.
- Aliments fonctionnels : Le gingembre est de plus en plus souvent incorporé dans les aliments et boissons fonctionnels, tels que les smoothies, les barres énergétiques et le kombucha, en raison de ses effets bénéfiques sur la santé.
Europe (Allemagne)
Préférences :
- Applications culinaires : Le gingembre est largement utilisé dans la cuisine allemande, en particulier dans la pâtisserie (pain d'épices) et dans la préparation de boissons telles que le thé au gingembre et la bière au gingembre.
- Utilisations médicinales : Il existe une forte tradition d'utilisation du gingembre en médecine naturelle pour ses propriétés anti-nauséeuses et anti-inflammatoires.
- Produits de bien-être : Le gingembre est populaire dans les produits de bien-être, y compris les compléments alimentaires, les tisanes et les produits de soins de la peau.
Tendances :
- Gingembre biologique : Comme aux États-Unis, l'Allemagne connaît une demande croissante de gingembre biologique, motivée par des préoccupations liées à la santé et à l'environnement.
- Produits innovants : Le marché connaît un afflux de produits innovants à base de gingembre, tels que les chocolats infusés au gingembre, les sirops de gingembre et les boissons alcoolisées aromatisées au gingembre.
- Durabilité : Les consommateurs accordent de plus en plus d'importance à la durabilité, d'où une préférence pour le gingembre issu du commerce équitable et de fermes respectueuses de l'environnement.
Japon
Préférences :
- Excellence culinaire : Le gingembre frais est très apprécié pour son utilisation dans les plats traditionnels japonais, tels que les sushis, les cornichons et les soupes.
- Produits de santé : Le gingembre est populaire dans les produits de santé, y compris les remèdes à base de plantes et les thés de bien-être, en raison de son utilisation de longue date dans la médecine traditionnelle.
- Variétés de haute qualité : Les consommateurs japonais préfèrent des variétés spécifiques de gingembre de haute qualité qui répondent à leurs exigences culinaires.
Tendances :
- Produits de qualité supérieure : Il existe un marché solide pour les produits à base de gingembre de qualité supérieure qui offrent des saveurs uniques et une grande qualité.
- Aliments fonctionnels : Le gingembre est incorporé dans les aliments fonctionnels, tels que les boissons santé et les compléments énergétiques, qui sont très prisés par les consommateurs soucieux de leur santé.
- Médecine traditionnelle : L'utilisation du gingembre dans le Kampo (médecine traditionnelle japonaise) est de plus en plus répandue, en raison de ses bienfaits pour la digestion et le bien-être général.
Moyen-Orient (Arabie Saoudite)
Préférences :
- Les médecines traditionnelles : Le gingembre est largement utilisé dans la médecine traditionnelle du Moyen-Orient pour ses propriétés anti-inflammatoires et digestives.
- Utilisations culinaires : Il s'agit d'un ingrédient courant dans la cuisine du Moyen-Orient, utilisé à la fois dans les plats salés et les desserts.
- Produits de bien-être : Les produits de bien-être à base de gingembre, y compris les thés, les compléments et les remèdes naturels, suscitent un intérêt croissant.
Tendances :
- Suppléments de gingembre : La demande de compléments alimentaires à base de gingembre augmente car les consommateurs recherchent des remèdes naturels contre des affections courantes telles que l'indigestion et l'inflammation.
- Boissons saines : Les boissons infusées au gingembre, telles que le thé au gingembre et les boissons aromatisées au gingembre, sont de plus en plus populaires en raison de leurs effets bénéfiques sur la santé.
- Remèdes naturels : L'utilisation du gingembre dans les remèdes naturels et homéopathiques est de plus en plus répandue, conformément aux pratiques traditionnelles de la région.
En comprenant les nuances du commerce mondial du gingembre, en adhérant aux normes de qualité et de conformité et en adoptant l'innovation, les exportateurs de gingembre peuvent tirer parti de la demande croissante pour cette épice polyvalente et recherchée.
Tout ce qui concerne les Gingers est ici :L'incroyable gingembre : Un guide indispensable.
